Practical Guide: 6 steps to optimise your Digital Shelf for conversational virtual assistants
In our previous article, we explored how voice searches are transforming the Digital Shelf and why brands need to adapt to this new conversational reality. We saw how consumers no longer type “cheap running trainers”, but instead ask “What are the best running trainers for under 50 euros?”.
Now it’s time to move from conceptual understanding to practical implementation. This guide will provide you with six concrete, actionable steps to optimise your Digital Shelf and make your products discoverable and recommendable by virtual assistants.
Each step includes specific tools, proven techniques and real-world examples that you can apply immediately to your digital strategy. By the end of this guide, you will have a clear roadmap to transform your digital presence and capture the opportunities offered by conversational commerce.
6 steps to optimise your Digital Shelf for virtual assistants
Step 1: Research conversational keywords
Keyword research for voice search requires a completely different approach to the traditional one. While traditional research focuses on short, direct terms, voice optimisation needs to understand how your customers actually speak when they ask questions.
Start by analysing the queries your current customers make to your customer service team. These real conversations reveal exactly how they formulate their questions and what information they are looking for. If you sell electronics, you probably receive questions like “what mobile do you recommend for taking good photos that isn’t too expensive?” instead of written searches like “cheap camera mobile”.
Use tools like AnswerThePublic to discover what questions users are asking about your sector. By entering a keyword, you will get hundreds of real queries organised by type: what, how, when, where and why. Many of these reflect voice search patterns. Google Trends also allows you to identify growing conversational queries. Explore the related terms and review the “related queries” and “related topics”, especially those with question words or phrases like “best”, “compare” or “near me”.
Analyse your product reviews on different platforms. Customers often use the same language they would in a voice search. Phrases like “perfect for beginners” or “ideal for small spaces” can inspire your content. Make a list of real-world use scenarios. Imagine your customers searching for your products while cooking, driving or exercising. Each situation creates different nuances in the searches that you must take into account.
Step 2: Include long-tail keywords and frequently asked questions
The keywords known as long-tail become the fundamental element of voice optimisation. These long, specific phrases perfectly match the conversational nature of voice searches and tend to have a clearer purchase intent.
Develop a comprehensive library of frequently asked questions that goes beyond the typical queries about delivery and returns. Include questions about product comparisons, specific use cases, compatibility, maintenance and troubleshooting. For example, if you sell vacuum cleaners, don’t just answer “how much is delivery?”, but also “which vacuum cleaner is best for homes with pets?” or “how do I know if a robot vacuum will work well in my home?”. Structure your answers in a way that can be easily extracted by virtual assistants. Start each answer with a clear, direct sentence that specifically answers the question. Then provide additional details. This structure makes it easier for algorithms to identify the main answer and use it in voice searches.
Incorporate natural variations of the same query. People formulate the same question in multiple ways. Some will ask “what is the best camera for beginners?”, others “what camera do you recommend for someone who is just starting out?” and others “what is the easiest camera to use for novices?”. Your content should capture these natural variations.
Additionally, create content that answers the intent behind each query. A question like “how long does this mobile’s battery last?” isn’t just looking for a number of hours, but an understanding of whether the phone will meet their daily needs. Your answer should address both aspects: the technical data and its practical meaning.
Step 3: Enrich your product pages (PDPs)
The product detail pages must be transformed into comprehensive informational resources that answer all the questions a virtual assistant might need to recommend your product. This transformation requires a strategic restructuring of the information.
Develop specific sections that answer common conversational questions. Include sections like “Who is this product for?”, “How do you use it?”, “What makes it different?” and “What do I need to know before buying?”. These sections provide exactly the type of information that virtual assistants look for to answer specific queries.
Optimise the technical specifications so they are understandable to both humans and algorithms. Instead of just listing “RAM: 8GB”, explain “This phone includes 8GB of RAM, enough to run multiple applications simultaneously without slowing down”. This approach helps virtual assistants to provide useful context in their answers.
Implement a robust comparisons section. Users frequently ask about differences between similar products by voice. Include clear comparisons with competing products or with other models in your own line. Use structured tables that virtual assistants can easily interpret.
Enrich visual content with detailed descriptions. Voice assistants cannot “see” images, but they can access the alt text and descriptions. Ensure that each image has a descriptive alt text that explains what is seen in the image and also what benefits the product has.
Regularly update availability and pricing information. Virtual assistants value the accuracy and timeliness of information. Implement systems that automatically keep information such as stock, prices and delivery options up to date.
Step 4: Implement structured data (Schema Markup)
Structured data acts as the secret language that allows virtual assistants to understand exactly what you are selling and how to present that information to users. Schema Markup is code you can add to your website to help search engines get better results for users.
Start by implementing basic product markup (Product Schema). This markup includes essential information such as product name, price, availability, description, brand, model and category. Virtual assistants use this data to provide accurate answers about prices and availability when users ask about specific products.
Add review and rating markup (Review Schema). Virtual assistants frequently mention ratings when recommending products. Correct review markup allows this information to be easily accessible and usable by voice algorithms.
Use FAQ markup (FAQ Schema) to structure your question-and-answer content. This type of markup is especially valuable because it directly matches the conversational nature of voice searches. When you implement an FAQ schema correctly, you significantly increase the chances of your answers appearing in Featured Snippets or Google’s Position Zero.
Don’t forget breadcrumb markup (Breadcrumb Schema) to help virtual assistants understand the structure and hierarchy of your website. This is especially important for e-commerce sites with multiple product categories and subcategories.
You can use a tool like Google’s Schema Markup Testing Tool to verify that your implementation is correct. Errors in the markup can cause virtual assistants to ignore your content completely, so correct implementation is crucial.
Step 5: Focus on local SEO
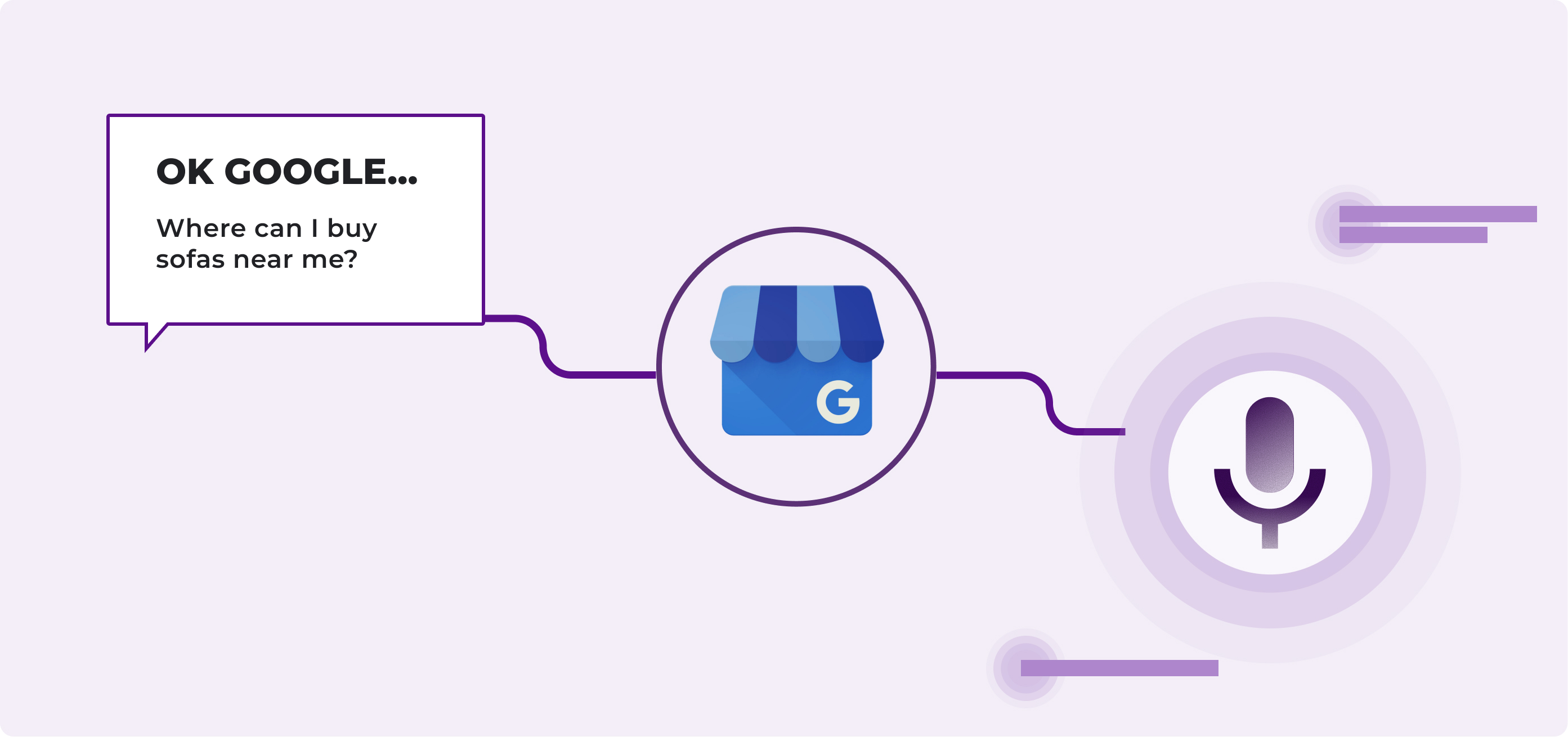
Local SEO takes on a whole new dimension in the context of voice searches. Users frequently include geographical references in their voice queries, even when they wouldn’t include them in written searches. “Where can I buy this product near me?” is one of the most common voice queries.
Optimise your Google Business Profile with complete and up-to-date information. Include not only basic data like address and opening hours, but also detailed descriptions of your products and services using natural language. Virtual assistants pull information directly from these profiles to answer local queries.
Implement specific pages for different locations if you have multiple points of sale. Each page should include unique information about that specific location, available products, special services and any distinctive features. Avoid duplicate content between pages for different locations.
Incorporate natural geographical references into your content. Instead of simply mentioning your address, include references to neighbourhoods, well-known landmarks and service areas. Create content that responds to specific local queries. Include pages that answer questions like “what shops sell X product in [your city]?” or “where can I repair X near [your location]?”. This specific content positions you to capture voice searches with local intent.
Encourage and manage local reviews on multiple platforms. Virtual assistants consider local reviews as signals of authority and relevance. Respond to all reviews, both positive and negative, using natural language that can also be relevant for voice searches.
Use structured data markup specific to local businesses (Local Business Schema). Include information about service areas, accepted payment methods, accessibility and any special services like home delivery or in-store collection.
Step 6: Prioritise loading speed and mobile experience
Loading speed becomes critical in the context of voice searches because users expect immediate answers. Virtual assistants prioritise content from websites that load quickly, as this allows them to provide faster responses to users.
Implement speed optimisation techniques specifically designed for mobiles. This includes image compression, code minification, use of content delivery networks (CDNs) and strategic caching.
Implement Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) for critical content pages such as blog articles, FAQ pages and main product pages. This code ensures extremely fast loading times on mobile devices, which is especially valuable for voice searches.
Ensure that your design is completely responsive and provides an exceptional experience on mobile devices. This includes not only that the content adapts to the screen size, but that the navigation is intuitive and interactive elements are easily usable with your fingers. Also, optimise the information hierarchy for mobile consumption. Users who arrive at your site from a voice search are often looking for specific information quickly. Structure your content with clear headings, concise paragraphs and easily accessible key information.
Measuring success and looking to the future
Optimising for voice search requires going beyond traditional SEO metrics. To assess the real impact of your efforts, you need specific indicators that reflect how users interact through conversational commands.
A key metric is your presence in Featured Snippets, especially for queries formulated in natural language. Tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs allow you to track these appearances in the so-called Position Zero, where a voice assistant is most likely to choose your content as an answer.
Although Google Analytics does not explicitly distinguish voice searches, you can infer their origin by analysing long-tail and mobile traffic. Sessions with detailed, conversational phrases often indicate voice interactions. Complement this analysis with Google Search Console, identifying queries that generate impressions but few clicks; these may be opportunities to improve titles, descriptions or content relevance.
In addition, monitor how and when virtual assistants mention your brand. Perform active tests with different devices and document your visibility. This will give you a clear idea of how you are positioning yourself in the conversational ecosystem.
Looking ahead, voice assistants will become increasingly contextual and personalised, integrating with IoT devices and offering responses that are more tailored to individual preferences. At the same time, interfaces are evolving towards hybrid formats that combine voice and image, such as smart displays, opening up new possibilities for displaying products more attractively.
Therefore, your optimisation strategy will need to adapt to more complex, personalised and visual experiences. Being prepared for multiple contexts and devices will be key to standing out in the conversational commerce of the future.
Conversations that convert: the next step in your digital strategy
Optimising the Digital Shelf for virtual assistants is a strategic necessity in an increasingly conversational digital environment. Throughout this guide, we have covered six key steps to adapt your content, your product pages and your technical structure to the way consumers now express their needs: by speaking.
From researching natural keywords to implementing structured data, through to improving the mobile experience and local focus, each step brings you closer to a digital presence that is more visible, relevant and useful for those who search with their voice.
The change is already underway: virtual assistants are becoming smarter, searches more contextual and user expectations higher. Brands that get ahead of this transformation will improve their visibility and be better positioned to connect with their customers at key decision-making moments.
You now have the tools and knowledge to get started. It’s time to put it into practice and lead the change towards a more natural, useful and human search experience.